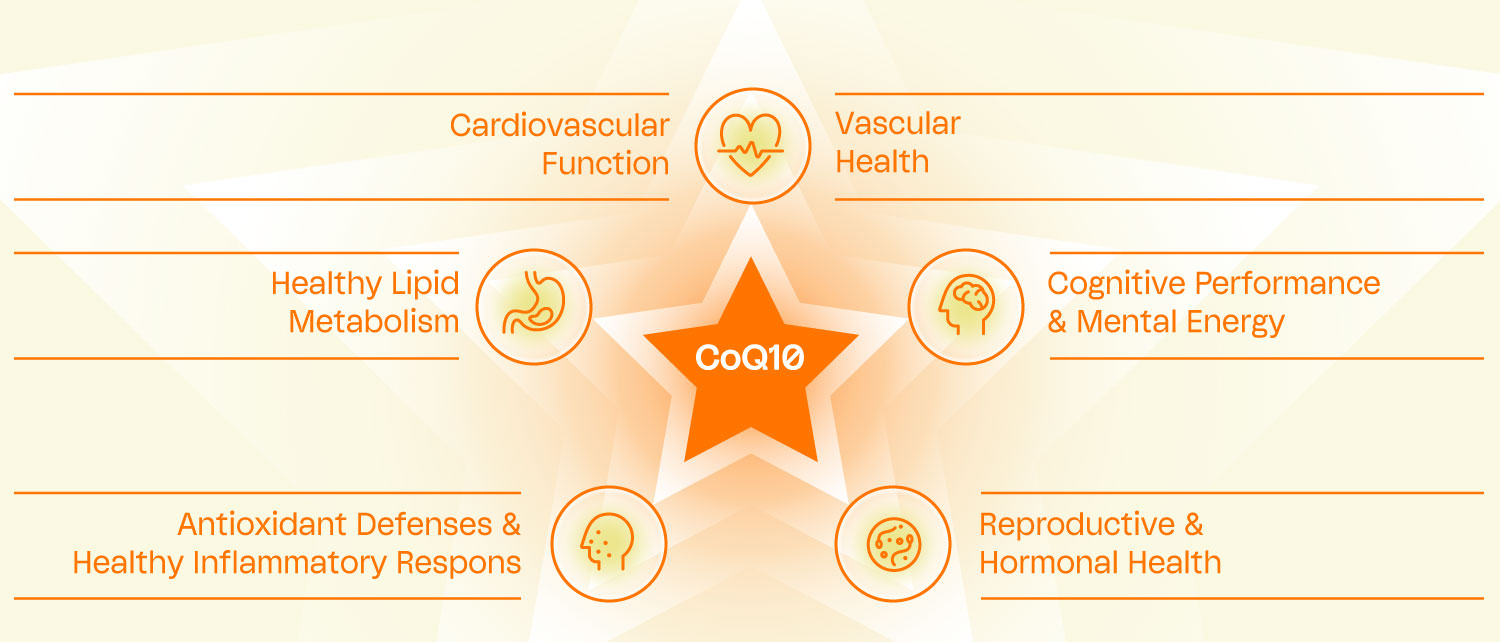
Enabling Smarter CoQ10 Products
For brands operating in an increasingly competitive supplement landscape, the challenge is no longer ingredient selection alone—but how effectively that ingredient is delivered and experienced.
Formulated using patented Concordix® emulsion technology developed in Norway to reflect the structural characteristics of nutrients as they occur in real food, CoQMax pairs established CoQ10 science with an advanced, food-mimetic delivery system designed to support consistent dosing, improve consumer compliance, and enable differentiated product design.
By addressing both the biological and practical limitations of conventional CoQ10 formats, CoQMax provides brands with a platform to develop next-generation cellular energy products — aligning credible science, modern delivery expectations, and real-world usability in a single solution.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making dietary changes or starting a new supplement. These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.